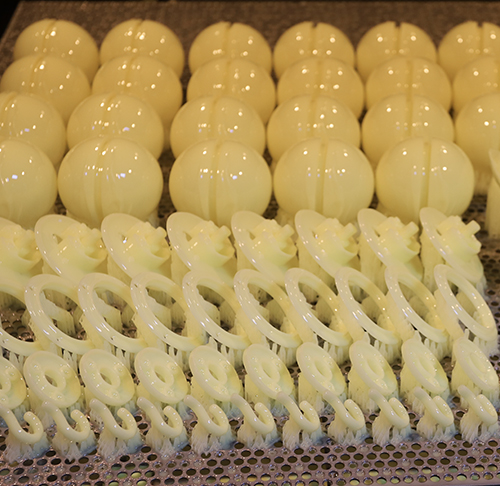
What is rapid prototyping
Rapid prototyping means making a physical sample of a new product design idea. This is done as a preliminary step towards eventual production, and is most useful when verifying that the finished product will look, feel, and perform as intended. New product developers turn to rapid prototyping for several reasons. They’re used for functional testing, approvals, design iterations, for crowdfunding campaigns, trade show models, and as a bridge to low-volume manufacturing.
Prototypes often inspire re-designs, improvements, and other modifications that may not have been obvious merely from a computer graphic, so in this regard they’re beneficial for optimizing a design before committing resources to larger volumes. In fact, being able to correct design errors early in the development phase can more than compensate for the cost of the prototype itself, so they’re wise investments.
What Are The Different Types Of Rapid Prototyping?
Any physical model can potentially be a prototype. The difference lies in how closely it reflects the intended finished part.
Very simple models can be made with paper, plastic, modeling clay, styrofoam, balsa wood, or other common household materials. These are examples of very low-fidelity prototypes, but they do have the advantage of being easy and inexpensive to make.
These types of prototypes would likely not function very well or for long, so they’re used primarily to get a visual idea of the design and to compare it in scale to other parts.
More high-fidelity prototypes use modern machine tools and materials, including various 3D printing technologies, vacuum casting, rapid tooling for injection molding, and CNC machining.
Prototypes often inspire re-designs, improvements, and other modifications that may not have been obvious merely from a computer graphic, so in this regard they’re beneficial for optimizing a design before committing resources to larger volumes. In fact, being able to correct design errors early in the development phase can more than compensate for the cost of the prototype itself, so they’re wise investments.
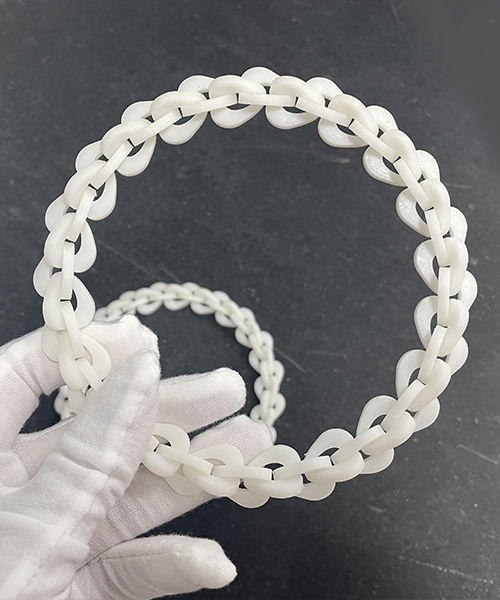
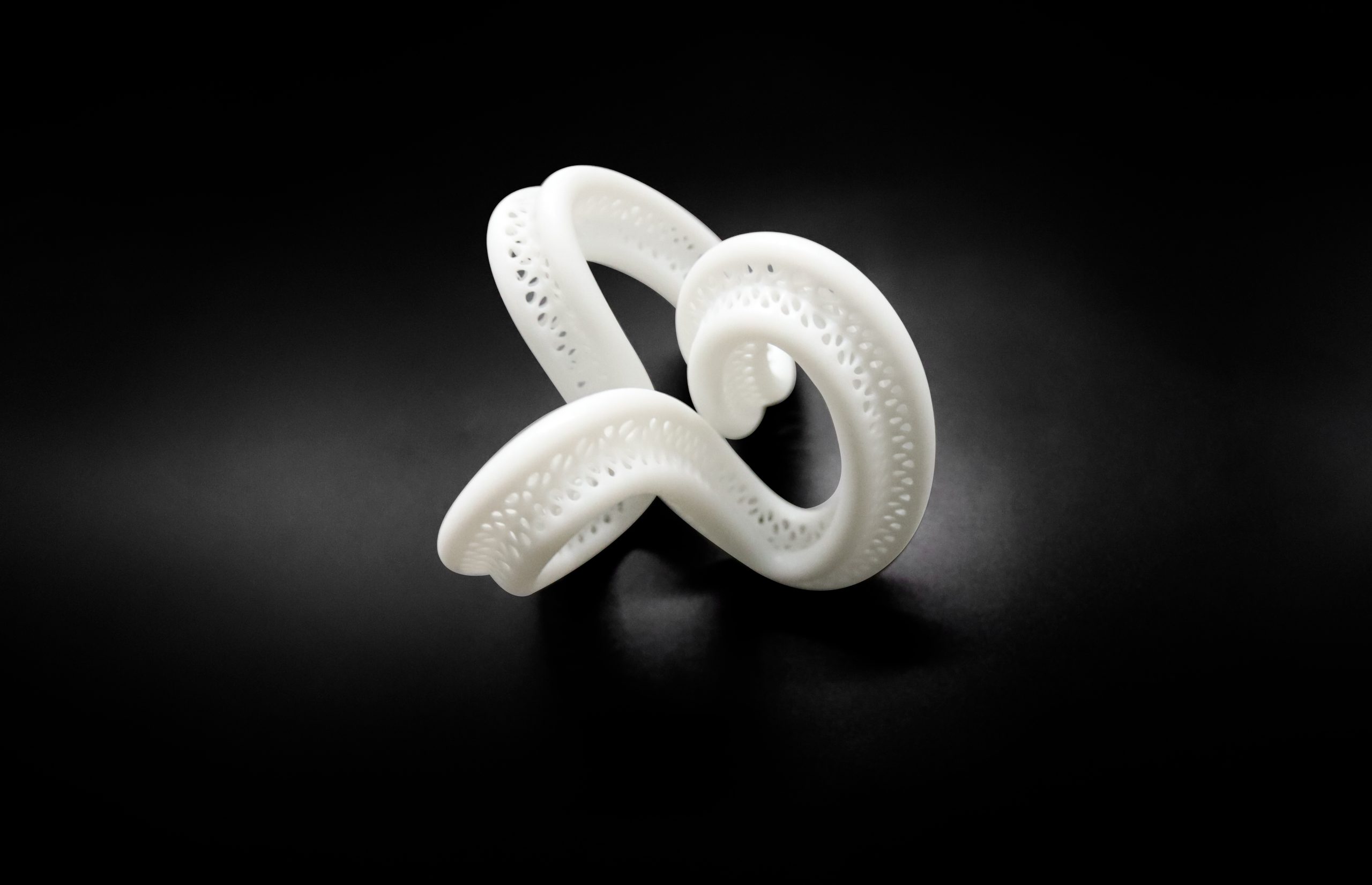


How To Choose The Right Rapid Prototyping Technique
The right prototyping method is the one that best fits your budget, the complexity of the part, what you want the prototype to do, and your development timeline. Better prototypes cost more money and take longer to make, but they also more faithfully represent the form, fit, and function of a production part.
The basic questions to ask are these:
- Will the prototype be a static display model?
- Does it need to be fully functional?
- Are there multiple, interconnected parts?
- What is the surface texture and finish?
- What is it made from?
- How important is strength and durability?
- How closely should it match the final production version?
There are many variables to consider and we cannot cover them all here.
WHY CHOOSE US
We recommend you contact our experts who can advise you on the method that is best for your application.
Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping Services FAQs
There are three common rapid prototyping services Star Rapid provides.
How to Choose
Correct rapid prototyping technology
Why Choose
Disadvantages
why did you choose us
浏览
客户案例
- Date
- 2024-10-15
- Date
- 2024-10-15
- Date
- 2024-10-15
GET IN TOUCH
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping means making a physical sample of a new product design idea. This is done as a preliminary step towards eventual production, and is most useful when verifying that the finished product will look, feel, and perform as intended. New product developers turn to rapid prototyping for several reasons. They’re used for functional testing, approvals, design iterations, for crowdfunding campaigns, trade show models, and as a bridge to low-volume manufacturing.
Prototypes often inspire re-designs, improvements, and other modifications that may not have been obvious merely from a computer graphic, so in this regard they’re beneficial for optimizing a design before committing resources to larger volumes. In fact, being able to correct design errors early in the development phase can more than compensate for the cost of the prototype itself, so they’re wise investments.
What Are The Different Types Of Rapid Prototyping?
Any physical model can potentially be a prototype. The difference lies in how closely it reflects the intended finished part.
Very simple models can be made with paper, plastic, modeling clay, styrofoam, balsa wood, or other common household materials. These are examples of very low-fidelity prototypes, but they do have the advantage of being easy and inexpensive to make.
These types of prototypes would likely not function very well or for long, so they’re used primarily to get a visual idea of the design and to compare it in scale to other parts.
More high-fidelity prototypes use modern machine tools and materials, including various 3D printing technologies, vacuum casting, rapid tooling for injection molding, and CNC machining.
Prototypes often inspire re-designs, improvements, and other modifications that may not have been obvious merely from a computer graphic, so in this regard they’re beneficial for optimizing a design before committing resources to larger volumes. In fact, being able to correct design errors early in the development phase can more than compensate for the cost of the prototype itself, so they’re wise investments.
How To Choose The Right Rapid Prototyping Technique
The right prototyping method is the one that best fits your budget, the complexity of the part, what you want the prototype to do, and your development timeline. Better prototypes cost more money and take longer to make, but they also more faithfully represent the form, fit, and function of a production part.
The basic questions to ask are these:
- Will the prototype be a static display model?
- Does it need to be fully functional?
- Are there multiple, interconnected parts?
- What is the surface texture and finish?
- What is it made from?
- How important is strength and durability?
- How closely should it match the final production version?
There are many variables to consider and we cannot cover them all here.