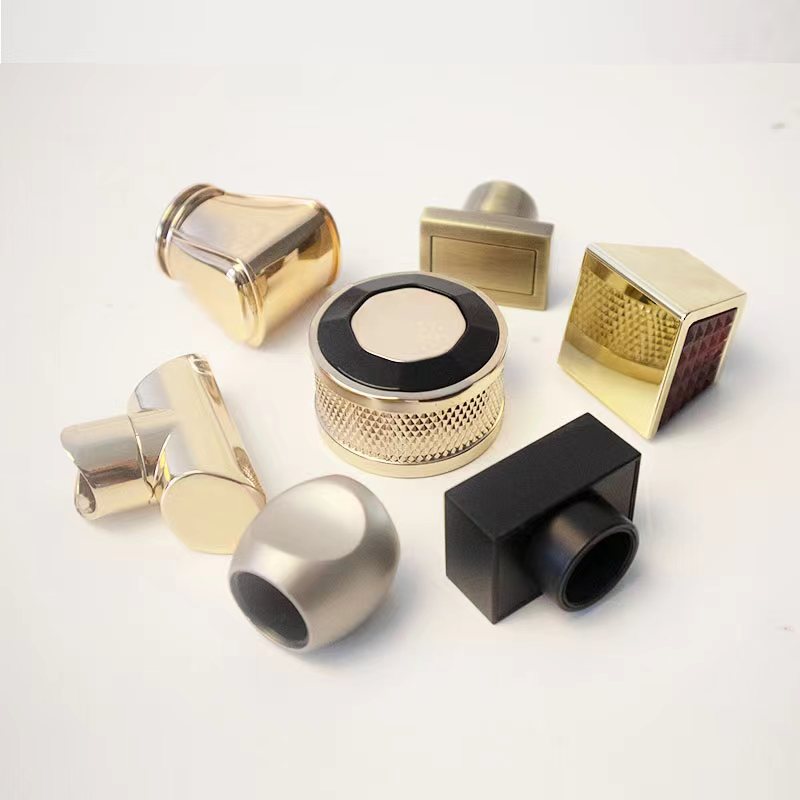
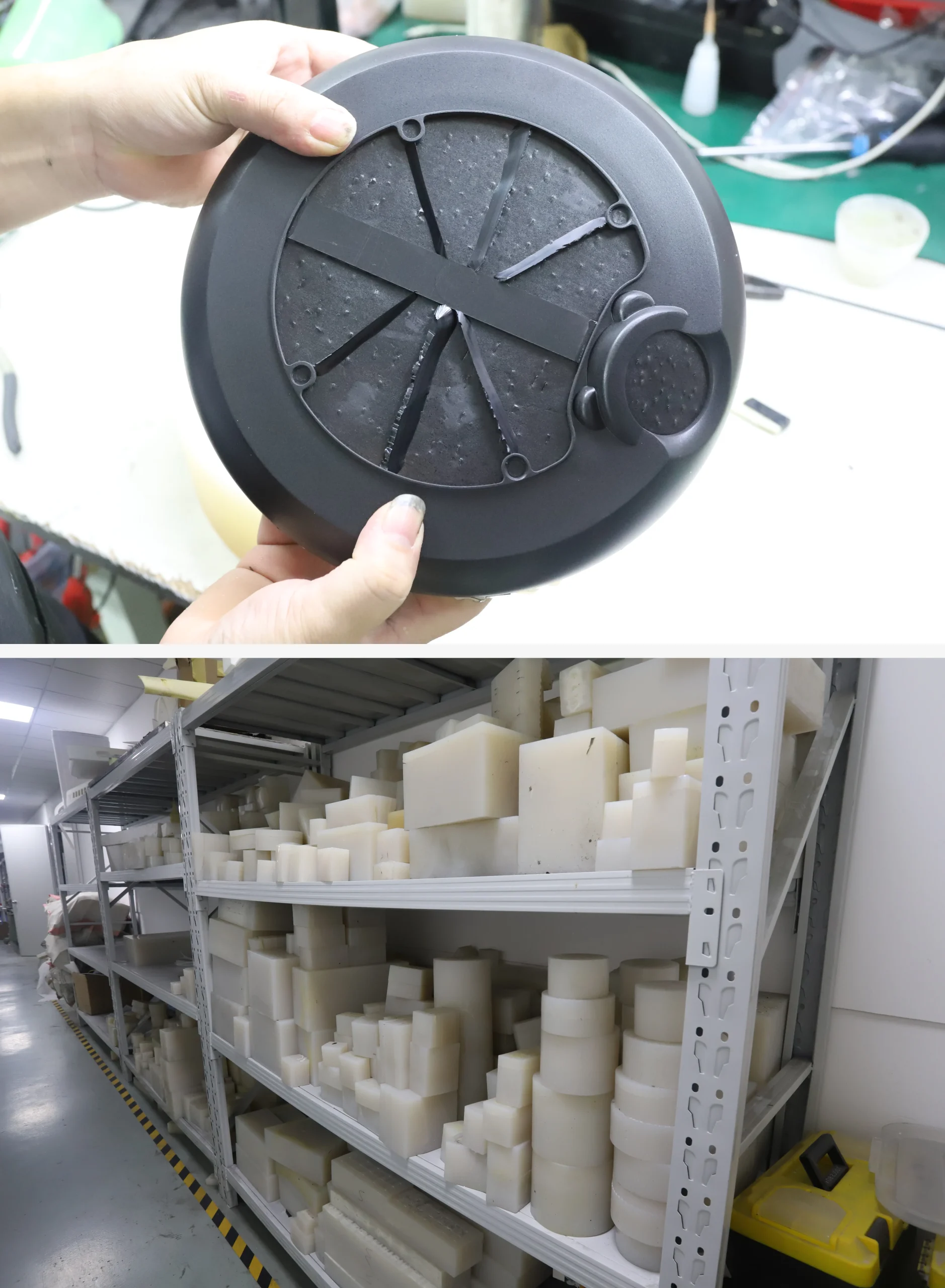
Vacuum casting is carried out under vacuum conditions to produce first class castings with no bubbles, smooth texture and no defects.
"Polyurethane casting, sometimes called vacuum casting, is a small batch casting process that is widely favored for its adaptability. Its use is critical for everything from medical devices to automotive and aircraft interior parts."
The vacuum casting process involves shaping a variety of air-free resins, including polyurethane, epoxy or silicone, into the desired shape. During this process, a pump or similar device will pull all the air out of the mold.
It offers many advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, including lower costs, faster production times, and the ability to produce complex parts with complex details.
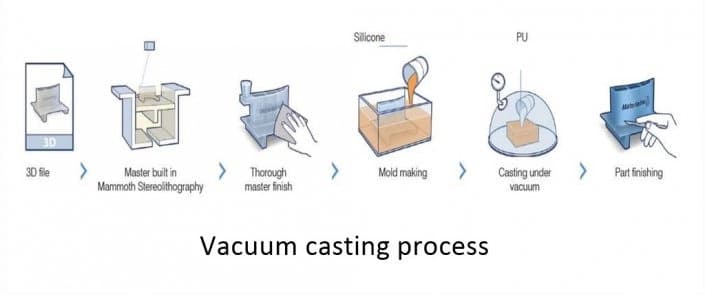
Vacuum casting

Vacuum casting process flow
1. Create 3D shapes or geometric shapes through modeling.
2.Use the 3D model as a guide to create a high-quality master model.
3.According to the master model, create a silicone mold.
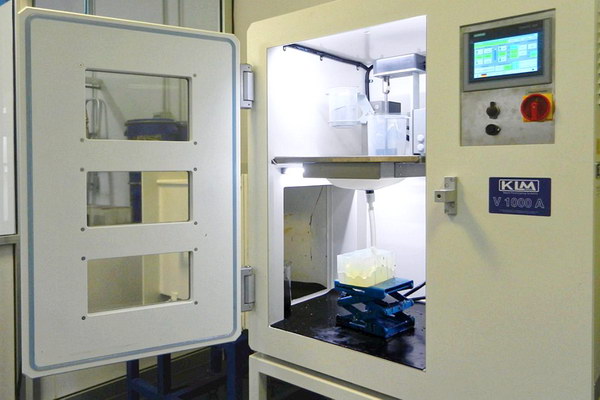
4.The casting material is mixed and poured.
5.Finish castings after curing and demoulding.

3D Modeling
Build Master Model
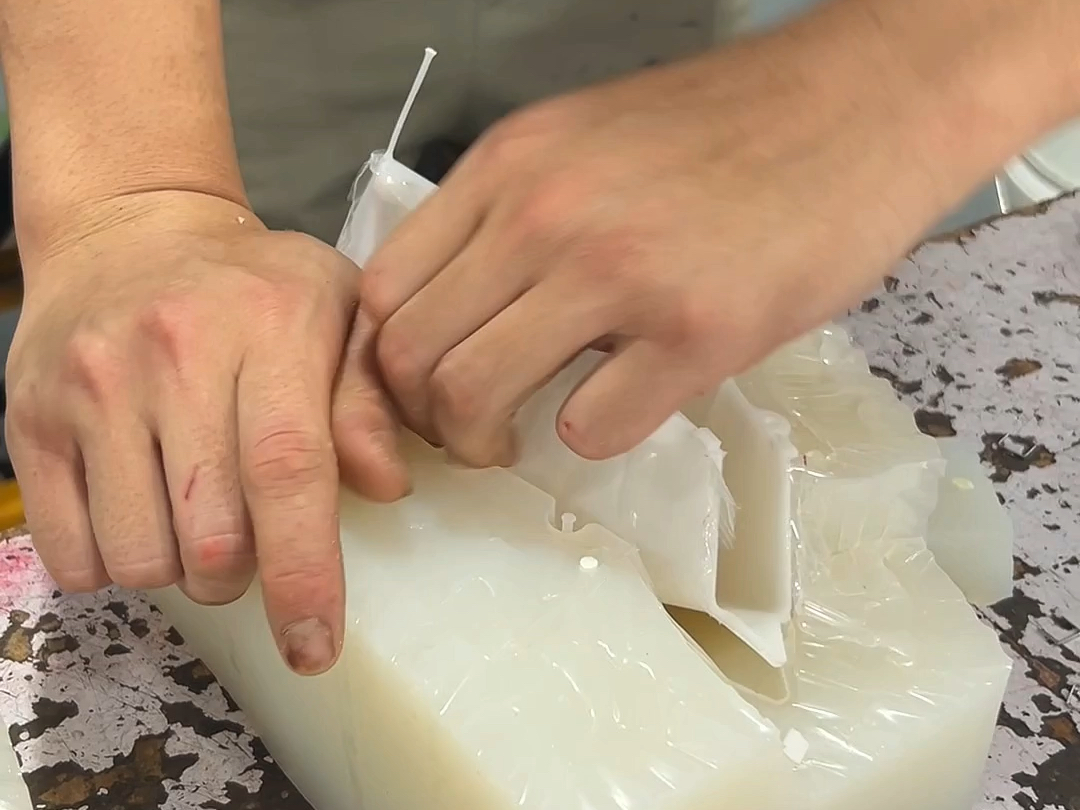

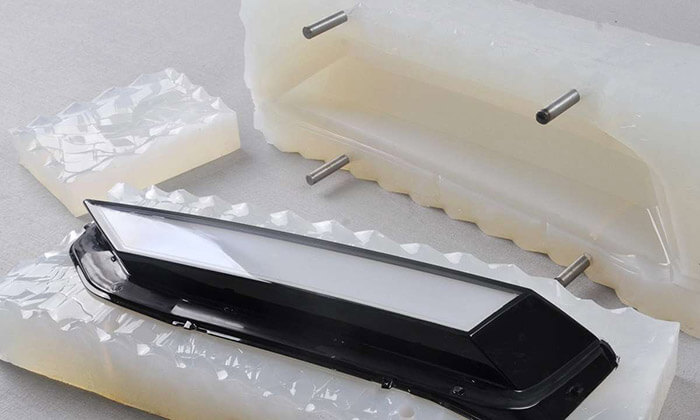
Make Silicone Mold
Casting materials are mixed and poured
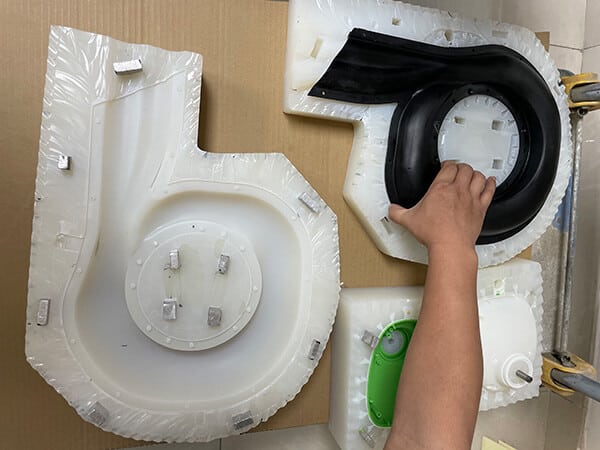


Casting curing and demoulding
Application of vacuum casting
Vacuum casting process is used in various industries because of its versatility. Its ability to produce complex and accurate components makes it ideal for delivering superior results.
1. Aerospace industry
Due to its accuracy, repeatability, and ability to handle complex details, vacuum casting can successfully manufacture precision aviation components, including fuel systems, air ducts, and aircraft exterior components.
2. Medical equipment
Vacuum casting is ideal for the manufacture of complex parts and components in the medical field, such as medical implants and prosthetics.
3. Automobile industry
Highly detailed automotive components, such as intake manifples, exhaust systems and body panels, can benefit from the precision and consistency of silicone vacuum casting in the automotive industry.
4. Food and beverage industry
Vacuum casting is commonly used by the food and beverage industry to produce food packaging, containers, cans, cups, bottles, glasses and other necessities in food production facilities.
5. Electronics industry
The shock and heat resistance of polyurethane makes vacuum casting the first choice for the manufacture of electronic device housings.
6.Consumer goods manufacturing
Consumer goods, such as toys and sports equipment, can be perfectly manufactured and suitable for application by the vacuum casting process.